Diving into the loan approval process, get ready for a journey filled with steps, timelines, and key factors that shape the financial world.
Unraveling the mysteries behind what it takes to get that coveted loan approval and how to navigate the process like a pro.
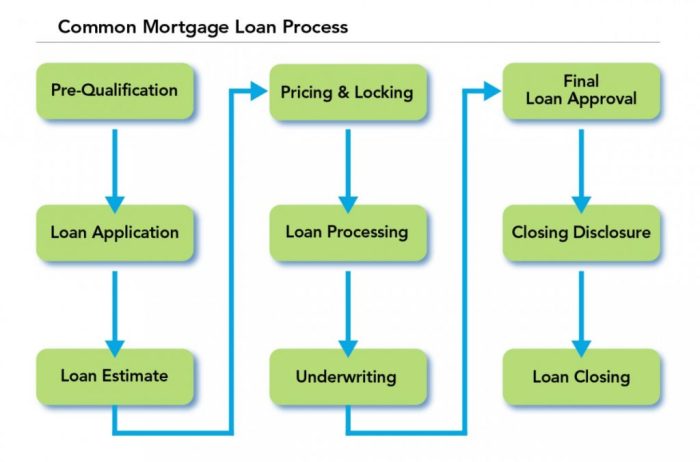
Loan Approval Process Overview
When applying for a loan, there are several steps involved in the approval process. First, the borrower submits an application with all necessary documentation, such as proof of income, credit history, and personal information. The lender then reviews the application to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
Steps Involved in the Loan Approval Process
- The lender reviews the borrower’s credit score and history to determine risk.
- Income verification is conducted to ensure the borrower can afford the loan.
- The property or asset being financed is appraised to determine its value.
- A decision is made by the lender to approve or deny the loan based on the information provided.
Typical Timeline for Loan Approval
- The loan approval process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application.
- Factors such as the lender’s workload, the borrower’s responsiveness, and the type of loan can affect the timeline.
- It is important for borrowers to be proactive in providing any additional documentation requested to expedite the process.
Key Factors Influencing Loan Approval Decisions
- Credit score and history play a significant role in determining loan approval.
- Income stability and debt-to-income ratio are also important factors considered by lenders.
- The type of loan, loan amount, and down payment can impact approval decisions.
- Collateral may be required for certain types of loans to mitigate risk for the lender.
Required Documentation
When applying for a loan, it’s crucial to have all the necessary documentation in order. Lenders require specific documents to assess your financial situation and determine your eligibility for a loan. Here are some common documents you will need to provide during the loan application process.
List of Common Documents
- Proof of Income: This can include pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements. Lenders use this to verify your ability to repay the loan.
- Identification: A government-issued ID such as a driver’s license or passport is required to confirm your identity.
- Credit Report: Lenders will pull your credit report to assess your creditworthiness and history of repaying debts.
- Employment Verification: Proof of employment, such as a letter from your employer or recent pay stubs, helps lenders verify your stability and income source.
- Asset Information: Details of any assets you own, such as property, vehicles, or investments, may be required to assess your overall financial health.
Importance of Each Document
- Proof of Income: Demonstrates your ability to make regular loan payments.
- Identification: Confirms your identity and prevents fraud in the application process.
- Credit Report: Provides insight into your credit history and helps lenders evaluate risk.
- Employment Verification: Validates your income source and job stability.
- Asset Information: Gives lenders an overview of your financial assets and net worth.
Tips for Organizing Documents
- Start early and create a checklist of required documents to stay organized.
- Keep all documents in a safe and easily accessible place to avoid last-minute scrambling.
- Make copies of all original documents to have backups in case anything gets lost.
- Label each document clearly to ensure the lender can easily identify and process them.
- Double-check all documents for accuracy and completeness before submitting your loan application.
Credit Score and Credit History
When it comes to getting approved for a loan, your credit score and credit history play a major role in the decision-making process. Lenders use this information to assess your creditworthiness and determine the level of risk involved in lending to you.
Impact of Credit Score and Credit History
- Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, based on factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and new credit inquiries.
- A higher credit score indicates that you have a history of responsible credit management, making you a less risky borrower in the eyes of lenders.
- On the other hand, a lower credit score may signal potential financial challenges or a history of missed payments, which can make it harder to get approved for a loan or result in higher interest rates.
Improving Credit Score
- Pay your bills on time and in full to establish a positive payment history.
- Keep your credit card balances low and avoid maxing out your credit limits.
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts within a short period, as this can lower your average account age and impact your credit score.
- Regularly review your credit report for errors and dispute any inaccuracies to ensure your credit information is up to date.
Lenders’ Use of Credit Information
- Lenders use your credit score and credit history to assess your risk level as a borrower and determine the terms of your loan, including the interest rate and loan amount.
- They may also look at other factors such as your income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio to make a more informed decision about your loan application.
- Having a strong credit score and positive credit history can increase your chances of loan approval and help you secure more favorable loan terms.
Income Verification
When applying for a loan, one crucial aspect that lenders look at is the applicant’s income. This helps them assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. Here, we will discuss the methods used for income verification, the importance of accurate income verification, and tips for a smooth verification process.
Methods Used for Income Verification
- Lenders may request pay stubs or W-2 forms to verify regular income.
- Self-employed individuals may need to provide tax returns or profit and loss statements.
- Rental income, alimony, or other sources of income may also need to be documented.
Importance of Accurate Income Verification
- Accurate income verification ensures that borrowers can afford the loan they are applying for.
- It helps prevent defaults and ensures that borrowers are not taking on more debt than they can handle.
- Lenders rely on accurate income information to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Tips for Smooth Income Verification
- Organize your financial documents in advance to speed up the verification process.
- Be transparent and provide all requested documents promptly to avoid delays.
- Communicate with your lender if you anticipate any challenges in providing income verification documents.
Loan Underwriting
Loan underwriting is the process where a lender evaluates the risk of lending money to a borrower and decides whether to approve the loan. It plays a crucial role in the loan approval process as it determines the terms and conditions of the loan.
Criteria Used by Underwriters
- Credit Score: Underwriters assess the borrower’s credit score to determine their creditworthiness. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk for the lender.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: This ratio helps underwriters evaluate the borrower’s ability to repay the loan based on their current debts and income.
- Employment History: Underwriters look at the borrower’s employment history to ensure a stable source of income for loan repayment.
- Collateral: For secured loans, underwriters consider the value of the collateral provided by the borrower to secure the loan.
Underwriting Standards for Different Loans
- Mortgage Loans: Underwriters for mortgage loans focus on the borrower’s ability to make timely mortgage payments and the value of the property being financed.
- Personal Loans: Underwriting standards for personal loans may place more emphasis on the borrower’s credit score and debt-to-income ratio.
- Business Loans: Underwriters for business loans may consider the business’s financial statements and the borrower’s business plan.
Loan Approval and Rejection: Loan Approval Process

When it comes to loan applications, there are three possible outcomes: approval, rejection, or conditional approval. Approval means you meet all the criteria and are deemed suitable for the loan. Rejection occurs when you do not meet the lender’s requirements. Conditional approval means you may still get the loan but need to fulfill certain conditions first.
Reasons for Loan Application Rejection
- Low credit score: A poor credit score indicates a history of missed payments or high debt, making you a risky borrower.
- Insufficient income: If your income is not enough to cover the loan payments, the lender may reject your application.
- Unstable employment: Lenders prefer borrowers with a stable job history to ensure repayment.
- High debt-to-income ratio: Having too much debt compared to your income can raise concerns about your ability to repay the loan.
What to Do After Loan Application Rejection
- Review your credit report: Check for any errors that may have contributed to the rejection and work on improving your credit score.
- Reduce debt: Lowering your debt levels can improve your debt-to-income ratio and make you a more attractive borrower.
- Increase income: Consider ways to boost your income to meet the lender’s requirements.
- Seek alternative lenders: If one lender rejects your application, explore other options with different criteria.





