Investment strategy is crucial in navigating the financial world. From defining what it entails to exploring different types and risk management, this guide dives into the essentials of creating a successful investment plan.
Introduction to Investment Strategy
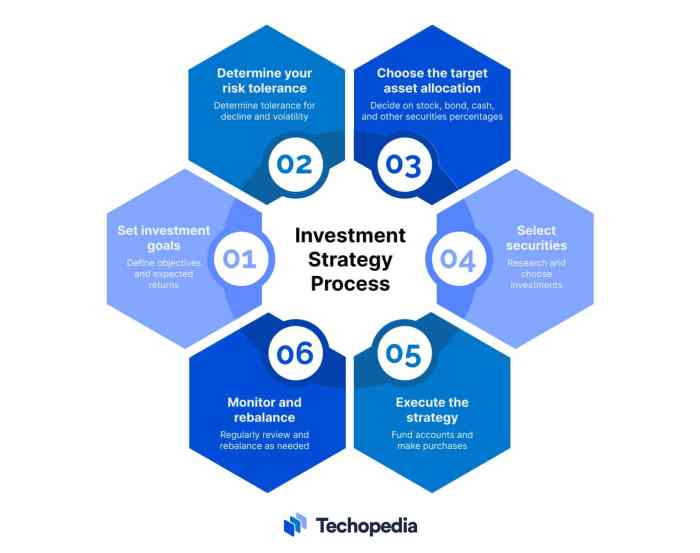
Investment strategy refers to a plan or approach that an individual or organization follows to allocate their resources in order to achieve specific financial goals. It involves making decisions on where to invest money, how much to invest, and for how long.
Having a well-defined investment strategy is crucial for several reasons. First, it helps individuals or organizations align their investment decisions with their financial goals, whether it be saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding a child’s education. Second, it provides a roadmap for making informed investment choices, reducing the likelihood of impulsive decisions based on emotions or market trends. Lastly, a clear investment strategy can help manage risk and optimize returns over time.
Common Goals of Investment Strategy
- Building wealth over the long term
- Generating passive income
- Preserving capital and protecting against inflation
- Diversifying investments to spread risk
Types of Investment Strategies
Investors have a variety of strategies to choose from when it comes to investing in the stock market. Each strategy has its own unique characteristics and approach to generating returns. Let’s explore some of the most common types of investment strategies:
1. Value Investing
Value investing involves finding undervalued stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value. Investors following this strategy believe that the market has undervalued the stock and that it has the potential to rise in value over time. One of the most famous value investors is Warren Buffett, who has achieved remarkable success by investing in undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
2. Growth Investing
Growth investing focuses on investing in companies that have the potential for above-average growth in revenue, earnings, or cash flow. Investors following this strategy are willing to pay a premium for stocks of companies that are expected to grow at a faster rate than the market average. An example of a successful growth investor is Peter Lynch, who managed the Fidelity Magellan Fund and achieved outstanding returns by investing in growth stocks.
3. Income Investing
Income investing, also known as dividend investing, involves investing in stocks or other assets that generate a consistent income stream. Investors following this strategy prioritize stocks with high dividend yields and stable cash flows. One of the most well-known income investors is John Templeton, who focused on dividend-paying stocks and bonds to generate income for his portfolio.
4. Momentum Investing
Momentum investing involves buying stocks that have shown an upward trend in price, expecting that the trend will continue in the short to medium term. Investors following this strategy believe that stocks that have performed well in the past will continue to outperform in the future. A successful momentum investor is William O’Neil, who developed the CAN SLIM strategy focusing on stocks with strong earnings growth and positive price momentum.
Risk Management in Investment Strategy
When it comes to investing, risk management plays a crucial role in determining the success of an investment strategy. By carefully assessing and mitigating risks, investors can protect their capital and increase the likelihood of achieving their financial goals.
Assessing Investment Risks
- One strategy for assessing investment risks is to conduct a thorough analysis of the market conditions and economic factors that could impact the performance of an investment.
- Investors can also use tools like risk assessment matrices or risk profiling questionnaires to evaluate their risk tolerance and identify potential areas of vulnerability in their portfolio.
- By diversifying their investments across different asset classes and industries, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall portfolio.
Mitigating Investment Risks
- One common strategy for mitigating investment risks is to set stop-loss orders, which automatically sell a security if it reaches a certain price, limiting potential losses.
- Investors can also use hedging techniques, such as options or futures contracts, to protect their portfolio against adverse market movements.
- Regularly reviewing and rebalancing a portfolio can help investors stay on track with their financial goals and adjust their risk exposure as needed.
Impact of Risk Management on Investment Outcomes
- Effective risk management can lead to more consistent returns over time, as losses are minimized and capital is preserved during market downturns.
- On the other hand, poor risk management can result in significant losses and hinder the long-term growth potential of an investment portfolio.
- By incorporating risk management strategies into their investment approach, investors can improve their chances of achieving financial success and reaching their desired outcomes.
Diversification in Investment Strategy

Diversification is a key strategy in investing that involves spreading your investments across different assets to reduce risk. It is important in an investment portfolio as it helps minimize the impact of market volatility on your overall returns.
Asset Allocation, Investment strategy
Asset allocation is a common method of diversification where you divide your investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce the risk associated with a single asset class underperforming.
Sector Diversification
Sector diversification involves investing in different industries or sectors of the economy. For example, instead of putting all your money in technology stocks, you can also invest in healthcare, energy, and consumer goods sectors. This helps reduce the risk of sector-specific events affecting your portfolio.
Geographical Diversification
Geographical diversification means investing in assets across different regions or countries. By spreading your investments globally, you can reduce the impact of economic or political events in a single country on your portfolio. For example, investing in both domestic and international stocks can help protect your portfolio from country-specific risks.
“Diversification is like putting your eggs in different baskets to avoid having all your eggs in one basket.”





