Decentralized apps are taking the tech world by storm, offering a new way of approaching applications that put users in control. From blockchain to peer-to-peer networks, the journey of decentralized apps is as intriguing as it is groundbreaking.
As we dive deeper into this innovative concept, we uncover the defining features, benefits, challenges, and the technology that powers these game-changing apps. Brace yourself for a wild ride through the world of decentralized apps!
Overview of Decentralized Apps

Decentralized apps, also known as DApps, are applications that run on a decentralized network of computers rather than a single central server. This means that no single entity has control over the app or the data it processes, making them more secure and resistant to censorship.
Key characteristics of decentralized apps include:
– Decentralization: No central authority controls the app, providing increased transparency and security.
– Immutability: Data stored on the blockchain is tamper-proof, ensuring the integrity of information.
– Security: Due to the distributed nature of the network, decentralized apps are less vulnerable to cyber attacks.
– Tokenization: Many decentralized apps use tokens for transactions within the network, enabling a peer-to-peer economy.
Examples of popular decentralized apps in use today include:
– Ethereum: A blockchain platform that supports a wide range of decentralized applications, from finance to gaming.
– Uniswap: A decentralized exchange allowing users to swap various cryptocurrencies without a central intermediary.
– Decentraland: A virtual reality platform where users can buy, sell, and build virtual land using blockchain technology.
Benefits of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized apps offer a range of advantages over traditional centralized applications. Let’s dive into the key benefits below.
Enhanced Security
Decentralized apps provide enhanced security compared to centralized applications. In decentralized systems, data is distributed across a network of nodes, making it more difficult for hackers to compromise the entire system. Additionally, the use of blockchain technology in decentralized apps ensures that data is tamper-proof and resistant to unauthorized alterations.
Promotion of User Privacy and Data Ownership
Decentralized apps prioritize user privacy and data ownership. Unlike centralized apps where user data is stored on a single server controlled by a central authority, decentralized apps allow users to have more control over their personal information. Users can choose what data to share and retain ownership of their data at all times.
Technology Behind Decentralized Apps
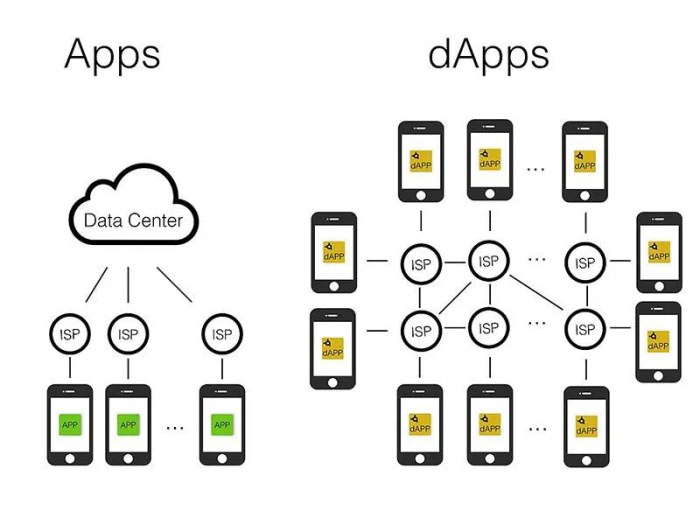
Decentralized apps (dApps) rely on innovative technologies to function efficiently and securely. These technologies include blockchain, smart contracts, and peer-to-peer networks, which play a crucial role in powering decentralized applications.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology serves as the foundation for decentralized apps by providing a secure and transparent decentralized ledger. Each transaction made within a dApp is recorded in a block, which is then linked to the previous blocks, forming a chain. This distributed ledger ensures data integrity and immutability, making it nearly impossible to tamper with or alter the information stored within the dApp.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce the terms of the agreement when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts play a vital role in decentralized apps by facilitating trustless transactions and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Peer-to-Peer Networks
Peer-to-peer networks enable decentralized apps to operate without a central authority. Instead of relying on a single server, dApps use a network of interconnected nodes to store and distribute data. This decentralized architecture enhances security, scalability, and resilience, as there is no single point of failure.
Consensus Mechanisms
Decentralized apps achieve consensus through various mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and more. These consensus algorithms ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
Examples of Blockchain Platforms
Some of the most commonly used blockchain platforms for decentralized app development include Ethereum, EOS, TRON, and Tezos. These platforms provide developers with the necessary tools and infrastructure to build and deploy decentralized applications efficiently.
Challenges in Decentralized App Development
Developing decentralized apps comes with its fair share of challenges that developers need to overcome in order to create successful applications in this space. From scalability issues to user experience challenges, here are some of the main obstacles faced in decentralized app development.
Scalability Issues, Decentralized apps
Scalability is a major challenge when it comes to decentralized applications. As the user base grows and more transactions are processed on the blockchain, the network can become congested, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher fees. This can hinder the overall performance of the decentralized app and impact user experience. Developers need to find efficient ways to scale their applications without compromising on security or decentralization.
User Experience Challenges
One of the key challenges for developers is creating a seamless user experience in decentralized applications. Unlike traditional apps, decentralized apps often require users to interact with the blockchain directly, which can be complex and intimidating for non-technical users. Developers need to design intuitive interfaces, provide clear instructions, and educate users on how to navigate the decentralized ecosystem. Improving the user experience will be crucial for mass adoption of decentralized apps.