Yo, peeps! Let’s dive into the world of flood insurance policies and break it down for ya. From what they are to why they matter, we got all the deets you need to stay informed.
Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of flood insurance policies and uncover the key aspects you should be aware of.
Overview of Flood Insurance Policies
Flood insurance policies are specialized insurance coverage that protect against property damage caused by flooding. They are important because standard homeowners insurance policies typically do not cover flood-related damages, leaving homeowners vulnerable in case of a flood.
Areas Requiring Flood Insurance
- Coastal regions prone to hurricanes and storm surges
- Low-lying areas near rivers or lakes
- Properties located in flood zones designated by FEMA
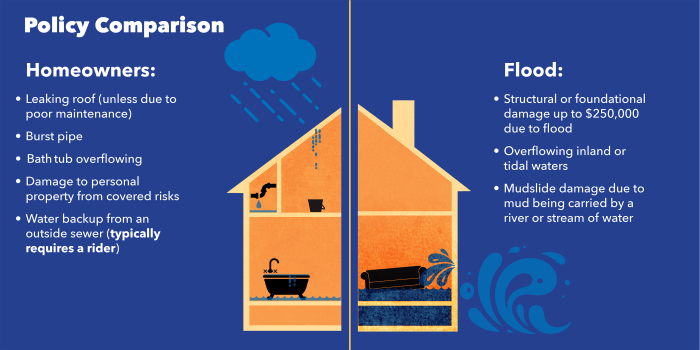
Regular Homeowners Insurance vs. Flood Insurance
Regular homeowners insurance typically covers damages from events like fire, theft, and certain types of water damage (e.g., burst pipes). However, it does not cover flood-related damages. Flood insurance specifically covers damages from flooding caused by natural disasters or heavy rain, providing an additional layer of protection for homeowners in at-risk areas.
Types of Flood Insurance Coverage
When it comes to flood insurance policies, there are different types of coverage available to protect your property and belongings. Let’s take a closer look at the options you have:
Building Property Coverage vs. Personal Property Coverage
- Building Property Coverage: This type of coverage helps protect the physical structure of your home or building, including the foundation, walls, roof, and built-in appliances. It typically includes coverage for damage caused by flooding, such as structural damage and water damage to the building itself.
- Personal Property Coverage: On the other hand, personal property coverage is designed to protect your belongings inside the building, such as furniture, clothing, electronics, and other personal items. This coverage helps replace or repair your possessions if they are damaged or destroyed by a flood.
Contents Coverage, Flood insurance policies
Contents coverage is a crucial component of flood insurance policies as it helps cover the cost of replacing or repairing your personal belongings that are damaged in a flood. This type of coverage typically includes items like furniture, appliances, clothing, and electronics. It’s important to take inventory of your belongings to ensure you have adequate contents coverage in your policy to protect your valuable possessions in case of a flood.
Factors Influencing Flood Insurance Premiums
When it comes to flood insurance premiums, there are several factors that can influence the cost. These factors can vary depending on the location of the property and the level of risk associated with potential flooding.
Location of Property
The location of a property is a key factor that can impact flood insurance premiums. Properties located in high-risk flood zones, such as coastal areas or regions prone to heavy rainfall, are likely to have higher premiums compared to properties in low-risk areas. Insurance companies assess the flood risk based on the property’s proximity to bodies of water, elevation, and historical flood data.
Mitigation Measures
Implementing mitigation measures can help lower flood insurance costs. Some examples of mitigation measures include elevating the property, installing flood vents, and implementing landscaping techniques to divert water away from the property. By taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of flooding, property owners can potentially lower their insurance premiums while also protecting their property from potential damage.
National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP)
The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) is a government initiative aimed at providing affordable flood insurance to property owners, renters, and businesses in communities that participate in the program. Established in 1968, the NFIP was created to reduce the financial impact of flooding on individuals and communities by promoting sound floodplain management and offering insurance protection against flood losses.
Purpose and Functions of NFIP
The NFIP determines insurance rates and coverage limits based on several factors, including the flood risk of the insured property, the location of the property in relation to flood zones, and the building’s elevation. Premium rates are set according to the property’s flood risk, with higher-risk properties typically paying higher premiums. Coverage limits are also determined based on the property’s flood risk, with more at-risk properties having lower coverage limits.
Role of Private Insurers
While the NFIP is the primary provider of flood insurance in the United States, private insurers also play a role in offering flood insurance policies. Some private insurers offer excess flood insurance policies that provide coverage above and beyond the limits set by the NFIP. These policies can be a valuable option for property owners in high-risk flood zones who require additional coverage beyond what the NFIP provides.





